What Is Meant by Pulp Capping Treatment?
Pulp Capping is a dental technique that intends to cover the exposed pulp chamber inside a tooth. The pulp chamber is a soft, non-calcified tissue in which a tooth’s nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissues reside. It is located at the hollow center of a tooth underneath the dentin layer.
When a tooth is extensively damaged due to trauma or penetration of cavities, the pulp might get exposed. The prolonged exposure of the pulp chamber makes it more susceptible to bacteria invasion. Depending on the severity of infection, dentists prefer the right reparatory works like pulp capping, root canal procedures to safeguard the tooth.
In this blog post, our dentists have explained the pulp capping procedure in detail. Keep reading to learn more.
When do dentists prescribe Pulp Capping?
Mostly, Root Canal Treatment is performed when a tooth has a deep cavity and it reaches the pulp chamber. RCT involves removing the pulp along with the connective tissues it holds. The empty pulp chamber is then filled and sealed. It prohibits the progression of microbial infections. Otherwise, the diseased tooth has to be extracted surgically.
However, if the pulp is not infected but is exposed due to decay or traumatic injury, the low-invasive procedure called “pulp cap treatment” is mandatory. It involves placing a sedative material to cover and protect the pulp from further microbial infections.
Depending on the extent of decay and tooth type, dental doctors the appropriate type of pulp capping to restore the tooth.
What are the different types of Pulp Capping?
Pulp Capping is categorized into 2 types: Direct pulp cap procedure and Indirect pulp cap procedure. After removing the decayed areas of the tooth, dentists can decide what kind of pulp capping a patient needs.
1) Direct pulp capping
Direct pulp cap treatment is recommended when the pulp chamber is exposed. The treatment procedure involves:
The tooth’s damaged or infected parts are removed.
A sedative material is placed directly over the pulp. It protects the pulp tissue from noxious agents and makes the pulp’s cell-rich zone repair the dentin. Usually, dentin formation begins within 30 days after the pulp capping procedure is performed.
Next, a temporary or permanent filling is affixed to the tooth, sealing it so that its strength and structure can be restored.
2) Indirect pulp capping
If dentists found that the pulp chamber is not exposed even though caries move deep inside a tooth, indirect pulp cap procedure is required. The steps involved in this procedure include:
The decayed portions are removed and a small space to cover the pulp layer is left.
Now, the sedative filling material is applied to the dentin. It helps in remineralization to repair the decayed dentin layer. The healing process takes around 8 months. Until then, the patient will be provided a temporary restorative appliance to cover the tooth.
Later, dentists evaluate if the dentin is repaired and regenerated properly. If yes, a permanent restoration device is bonded to revamp the tooth’s structure as well as its strength.
Generally, the indirect pulp capping procedure is prescribed if a tooth is deeply infected but the pulp does not show any signs of infection.
What are the sedative filling materials used in pulp capping treatments?
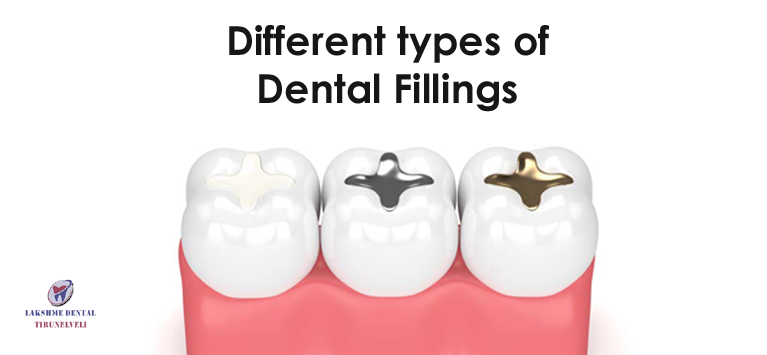
The sedative fillings (also known as pulp capping agents) used in this treatment are protective biocompatible materials. This is the reason why dentists place them directly for protecting the pulp layer. The wide range of materials used for pulp capping are listed here:
- Calcium Hydroxide
- Mineral trioxide aggregate
- Glass ionomer
- Zinc Oxide Eugenol (ZOE)
- Dentin-bonding agent
Pulp capping is a minimally invasive procedure performed to treat pulp exposure. In certain cases, it prevents the need for root canal procedure. It is more cost-effective than endodontic treatments and helps you to preserve a tooth that is severely injured or badly infected. It has ensured success rates and avoids further complex procedures in most cases.